What Are Biogas Generators: A Beginner’s Guide
What Are Biogas Generators? A Beginner's Guide
What Are Biogas Generators? A Beginner's Guide
In this comprehensive beginner’s guide, we've explored the transformative power of the biogas generator, a remarkable piece of equipment that turns biodegradable waste into sustainable energy. These generators not only provide a practical solution for waste management but also contribute significantly to powering our homes and communities. By harnessing the energy potential of organic waste, biogas generators offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional energy sources, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impacts. As we look to the future, the role of the biogas generator in creating sustainable, renewable energy solutions becomes increasingly vital, marking a significant step towards a greener, more sustainable world.
Have you ever wondered how the stuff we toss out can turn into something useful? Welcome to the world of the biogas generator, where waste isn't just rubbish – it's a treasure trove of energy. These ingenious systems use everyday waste to produce gas – a clean, renewable energy source.
At the heart of a biogas generator are bacteria. These microscopic powerhouses work tirelessly, breaking down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It's a natural process, similar to what happens in swamps or even in your compost pile. But here's where it gets interesting: instead of letting this gas escape into the atmosphere, the biogas generator captures it. This gas – a mix of natural gas and other elements – can then be used to generate heat, electricity, or both.
So, why should you care? Because biogas generators are more than just a fancy way to deal with waste. They're a sustainable source of power that can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. And that's a big deal for our planet.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainable Energy Production: Biogas generators are innovative systems that convert organic waste into biogas, a clean and renewable energy source. This process not only offers an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels but also plays a crucial role in waste management, reducing landfill use and methane emissions.
- Versatile Applications: These generators are versatile, supporting various applications including electricity and heat generation, and even fuel for vehicles. They are utilised in diverse settings, from small-scale farm-based plants to large commercial and industrial facilities, demonstrating their adaptability and significance in the renewable energy landscape.
- Economic and Environmental Benefits: While biogas generators require an initial investment, they offer long-term economic benefits through energy savings, potential revenue from excess energy production, and eligibility for subsidies and incentives. Environmentally, they contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a circular economy, aligning with global sustainability goals.
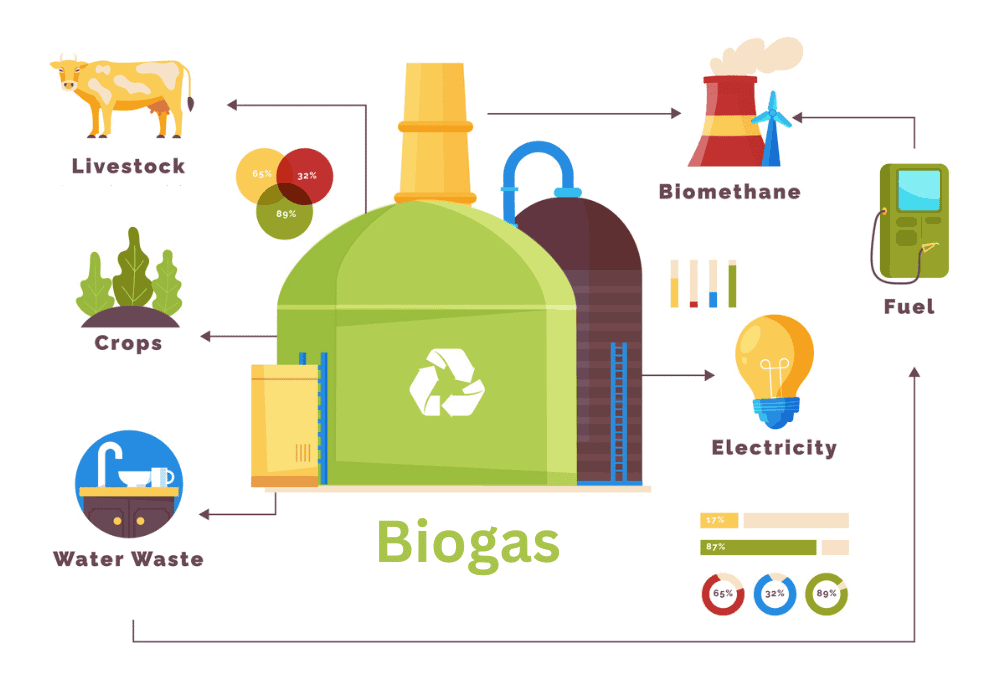
What is Biogas?
Biogas is a type of biofuel that is naturally produced from the decomposition of organic waste. When organic matter like leftover food, cow dung, or plant waste gets piled up without air (that's the anaerobic digestion part), it starts breaking down. What you get is biogas, a mix of mostly methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with traces of other gases like hydrogen sulfide and moisture.
The process of biogas production mimics nature's way of recycling organic materials. In the absence of oxygen, specialised microorganisms feed on the organic matter, breaking it down into simpler substances. This process not only produces biogas but also leaves behind a nutrient-rich residue called digestate, which can be used as a natural fertiliser.
Now, about methane – that's the key player in biogas. When burned, biogas releases energy, which can be used for heating, electricity generation, and even as a fuel for vehicles. Unlike fossil fuels, using biogas doesn't mess with the carbon dioxide balance of the planet. The carbon in biogas comes from plants that already took CO2 from the air. So, it's like returning what was borrowed – a closed loop.
Biogas production not only provides a sustainable way to manage waste but also contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By capturing methane that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere from decomposing waste, biogas generation helps mitigate the impact of potent greenhouse gases.
Now that we've uncovered the basics of biogas, let's explore the transformative process that allows biogas generators to turn waste into a powerful source of energy.

How Do Biogas Generators Convert Waste into Energy?
Biogas generators efficiently use organic waste to produce gas and power, turning everyday rubbish into valuable energy products. A biogas generator is a key solution in sustainable energy production. Let's explore how they work:
Starting with Organic Waste: The process begins with the collection of organic waste. This includes a variety of materials like food scraps from your kitchen, agricultural residue, manure from livestock, and even organic matter from landfills. This biomass isn't just rubbish; it's the raw material for biogas generators.
Creating an Anaerobic Environment: Next, this waste is placed in a biogas digester, a sealed container where oxygen is limited. This setup is crucial because it creates an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment. That's the environment these special bacteria need to kickstart the generation process.
Bacteria Get Busy: Inside this oxygen-free zone, bacteria are the unsung heroes. They break down the biomass, turning it into something valuable. It's a bit like fermentation, where these microorganisms digest the waste and transform it into simpler substances, crucial for biogas generation.
Production of Biogas: As these microorganisms work, they churn out biogas – a blend of methane (a key component of natural gas) and carbon dioxide. Methane is the powerhouse here; it's the fuel we want for energy.
Capturing the Power: The biogas generated is then captured and stored. Whether it's burning it for heat, converting it into electricity, or using it as vehicle fuel, it's all about harnessing power.
Managing Waste Efficiently: Not only does this process create a renewable source of energy, but it also plays a significant role in waste management. By converting organic waste into biogas, we reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Understanding the conversion of waste to energy leads us to the microscopic heroes of this process. Next, we'll delve into the critical roles that bacteria and biomass play in the production of biogas.
What Role Do Bacteria and Biomass Play in Biogas Production?
Biogas production is a remarkable process that hinges on the symbiotic relationship between bacteria and biomass. This process, known as anaerobic digestion, is a biological marvel where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas. Let's delve into how this happens and the types of biomass that fuel this eco-friendly energy source.
The journey begins with biomass, often composed of agricultural waste like animal manure, crop residues, and other organic plant materials. These forms of waste are not just byproducts; they are potent sources of energy waiting to be unlocked. In the anaerobic environment, specialised bacteria get to work. They digest the biomass, a process that occurs in stages. Initially, bacteria convert complex organic compounds in the biomass into simpler substances. Then, other bacterial groups further break down these substances. Throughout these stages, no oxygen is involved, which is crucial for the specific types of bacteria engaged in biogas production.
Specific microorganisms such as methanogens and sulfate-reducing bacteria perform anaerobic respiration, playing a critical role in biogas production. These organisms transform biomass waste into biogas (mainly methane and carbon dioxide) and digestate in biogas plants, which treat farm wastes or energy crops. The efficiency of biogas production can be enhanced in these plants, especially when wastewater is co-digested with other residuals from industries like dairy, sugar, or brewing.
Moreover, biogas production involves two key processes: mesophilic and thermophilic digestion, dependent on temperature. This shows how biogas production can be optimised or challenged in different climates, adding another layer of complexity to this sustainable energy source.
As the digestion progresses, the bacteria produce biogas, a mixture predominantly comprising methane and carbon dioxide. Methane, the primary component of biogas, is a significant source of energy. It can be harnessed and used similarly to natural gas, powering homes, fuelling vehicles, and generating electricity. This transformation from waste to gas is not just a disposal method for agricultural waste but a sustainable way to produce power. The efficiency of this process largely depends on the type and quality of biomass used. Optimal biomass types enhance the production of methane, thereby increasing the energy yield of the biogas.
Bottom line: bacteria and biomass are the unsung heroes in biogas production. They're turning what we'd normally toss out into something incredibly useful, all while keeping things green and sustainable.
With the importance of bacteria and biomass established, it's natural to wonder about the types of waste that can be utilised. Let's examine how home and food waste can be effectively transformed by biogas generators.

Can Biogas Generators Use Home and Food Waste Effectively?
Biogas generators offer a multifaceted solution to tackle household waste, especially food scraps by getting rid of waste and turning it into something valuable – energy. Let's dive into how these machines make the most out of everyday trash and the perks they bring, both for the planet and our daily lives.
Detailed Technical Process: Here's how they work. A biogas generator breaks down organic materials without oxygen through anaerobic digestion. They can handle a variety of materials – from your kitchen leftovers to industrial byproducts and even the sludge from wastewater treatment. The kind of waste you feed them and the generator model you've got play a big part in how well they work.
Stacking Up Against Other Solutions: Compared to other waste management and renewable energy solutions, the biogas generator stands out for its dual functionality - waste reduction and energy production. Plus, they're often better at handling organic waste and gentler on the environment than some other options.
Maintenance and Best Practices: Proper maintenance is crucial for the efficient operation of biogas generators. Sustainable practices, regular check-ups, and adherence to safety guidelines ensure that these systems function optimally, reducing risks and enhancing their longevity.
In conclusion, the biogas generator is effective in utilising home and food waste, offering a sustainable solution for energy needs while reducing landfill waste. They represent a practical and environmentally friendly approach to waste management and energy generation, with significant benefits for both the environment and the economy.
Having seen how biogas generators can turn our everyday waste into energy, we're poised to consider the broader impact. Let's shift our focus to the environmental benefits that these generators bring to the table
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using Biogas Generators?
The environmental benefits of using biogas generators are significant and multifaceted. A biogas generator will use organic waste to produce gas and power, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. By doing so, they provide numerous advantages for the environment and the people who rely on them. Let's delve into these benefits:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biogas generators significantly lower our carbon footprint by converting organic waste into biogas. This process prevents methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from being released into the atmosphere, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Lowering Reliance on Fossil Fuels: The adoption of biogas generators represents a pivotal shift towards sustainable power solutions. By generating energy from organic waste, we reduce our dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels, conserving natural resources and lessening the environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and use.
Contributing to a Circular Economy: The transformation of waste into valuable resources through biogas production exemplifies the principles of a circular economy. It's about striking a balance – boosting the economy without trashing the planet.
Diverting Organic Waste from Landfills: Biogas generators also tackle the landfill issue. By diverting organic waste to energy production, we're reducing methane emissions and solving two problems at once – waste and energy.
Preparing for a Sustainable Future: Looking ahead, biogas generators are a smart step towards a sustainable future. They're key to building an energy system that's tough, green, and ready for what's next.
Malaysia's Renewable Energy Transition: In Malaysia, the conversion of animal dung into biogas as part of its waste-to-renewable energy (WTRE) technologies has been a significant stride towards achieving renewable energy goals. This practical application of biogas technology demonstrates its effectiveness and benefits (1).
Global Impact of Biogas Generators: The adoption of biogas technology in developing countries plays a crucial role in achieving sustainable development goals, including providing energy, improving environmental security, and enhancing sanitation and health services (2).
Addressing Environmental and Health Concerns: But it's not all smooth sailing. Biogas generators, while beneficial, must address environmental and health concerns, such as emissions of nitrogen oxides and the importance of proper biomass and digestate storage (3).
Biogas in the Renewable Energy Context: In the big picture of renewable energy, biogas is a key player. It's tackling the energy crisis, and fighting against problems like resource depletion, global warming, and air pollution.
The environmental advantages of biogas are clear, but how exactly does the technology work? Next, we'll break down the inner workings of a biogas digester and its role in generating power and heat.
What are the Pros and Cons of Biogas Generators?
Biogas generators are transforming our approach to renewable energy and waste management, offering a sustainable solution by converting organic waste into valuable energy. These systems are not just about energy production; they embody a holistic approach to managing waste and reducing environmental impact. However, like any technology, they come with their own set of challenges and considerations.
Pros:
- Sustainable Energy Production: By converting organic waste into biogas, these generators provide a renewable source of energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Waste Management: They offer an effective way to manage organic waste, reducing landfill use and associated methane emissions.
- Economic Benefits: Beyond energy production, biogas systems can generate economic advantages through the production of biofertilisers and potential revenue from excess energy.
Cons:
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of setting up a biogas generator can be significant, potentially deterring smaller operations or individuals.
- Operational Expertise: Effective management and maintenance require specialised knowledge, adding complexity to their use.
- Variable Efficiency: The energy output from biogas generators can fluctuate based on the quality and quantity of organic waste available.
For a deeper dive into the nuanced world of biogas generators, exploring their benefits and challenges in detail, visit our page on the Balanced View: Pros and Cons of Biogas Generators.

How Does a Biogas Digester Work to Generate Power and Heat?
Biogas digesters are innovative solutions that transform organic materials into valuable energy resources. These systems use advanced techniques such as hydrate separation, cryogenic separation, and membrane enrichment to improve the quality of biogas, making it comparable to natural gas.
The Process of Biogas Production
The production of biogas happens in four steps: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis, with each step important for breaking down the waste and making biogas that's rich in methane.
Generation of Power and Heat
Biogas is used for heating or in combined heat and power units, where it fuels engines or turbines to generate electricity, with the excess heat utilised in various processes.
Applications in Domestic and Industrial Settings
Biogas digesters are beneficial in rural areas and industrial applications. They can take the place of regular natural gas, help keep things sustainable, and cut down on carbon emissions.
Real-world Applications and Benefits
In Europe, biogas digesters are already doing great things. They power local areas, handle waste, and reduce greenhouse gases. These examples highlight the practical benefits and versatility of biogas technology.
With a grasp on the function of biogas digesters, it's time to look at the nuts and bolts. We'll explore the equipment and technology that are essential for efficient biogas generation.
What Equipment and Technology Are Involved in Biogas Generation?
In the world of biogas generation, a variety of equipment and technology come together to make the process efficient and effective. At the core of this system is the biogas digester. These are large tanks where the magic of anaerobic digestion happens. Organic materials like food waste, manure, and farm waste are broken down by bacteria in these oxygen-free environments, producing biogas primarily composed of methane.
Next up are the storage tanks. Once the biogas is produced, it needs to be stored safely before it can be used. These tanks are designed to handle the pressure and composition of biogas, ensuring that none of the valuable energy is lost.
Now, what do we do with this biogas? We turn it into something we can use. Depending on the setup, this could mean converting biogas into electricity through generators heating up the home, or even refining biogas into biomethane, which can be used as a direct substitute for natural gas.
Technological advancements have played a significant role in making biogas generators more efficient and accessible. Innovations in digester design have improved the speed and efficiency of the anaerobic digestion process. Enhanced purification and storage technologies ensure that a higher quality of biogas is produced and retained. Moreover, advancements in energy conversion technologies have broadened the scope of biogas use, making it a more versatile and reliable source of renewable energy.
Biogas generation is a mix of smart tech and solid engineering. From the digesters where it all starts to the tanks and equipment that handle the end product, each part is crucial. And thanks to ongoing technology improvements, it's becoming an even better option for sustainable energy.
Equipped with knowledge about the technology behind biogas, let's turn our attention to the innovative applications that are pushing the boundaries of what biogas generators can do.
What are Some Cutting-Edge Applications of Biogas Generators?
Application innovation is just one piece of the puzzle. To truly appreciate the potential of biogas, we must also understand its economic landscape, particularly in the UK market.
Understanding the Economics of Biogas Generators in the UK
Initial Capital Investment Insights:
-
- Small-scale farm-based plants could require an investment of up to £1 million.
- For home biogas systems, the initial cost varies and can reach up to £6,000, depending on capacity and materials.
Operational Costs Breakdown:
-
- Operational expenses encompass maintenance, labour, backup electricity, and biogas upgrading.
- Annually, a small digester's maintenance could cost around £10,000.
Potential Savings and Revenue Opportunities:
-
- Biogas plants can offset costs by generating renewable energy, replacing fossil fuels, and selling surplus electricity or biomethane.
- Utilising biogas can lead to notable CO2 emission reductions, aligning with environmental goals and possibly earning carbon credits.
Subsidies and Financial Incentives in the UK:
-
- The Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) offers a fixed income for renewable heat generation, including biogas.
- The Renewable Transport Fuel Obligation (RTFO) mandates a certain percentage of fuel from renewable sources, supporting biomethane.
- The Green Gas Support Scheme (GGSS) is designed to foster new biomethane production, with a substantial annual budget.
The financial feasibility of biogas generators in the UK hinges on various factors like operation scale, technology, and feedstock. Despite the hefty initial costs, the blend of operational management, potential savings, and governmental incentives renders biogas generation an economically appealing renewable energy venture in the region.
Wrapping Up: A Future Using The Power of the Biogas Generator
As we conclude our journey through the world of the biogas generator, it's clear that these systems are more than just a means to manage waste. They represent a transformative approach to energy production, offering sustainable solutions that benefit both the environment and society. Biogas generators efficiently use organic waste, converting it into gas and power, thus reducing our reliance on traditional energy sources like natural gas and coal.
These systems not only alleviate the burden on your local landfill but also contribute to cleaner air and water. By processing organic waste, biogas generators prevent the release of harmful methane into the atmosphere, significantly cutting down greenhouse gas emissions. The power generated from these systems can light up homes, fuel industries, and even power vehicles, showcasing the versatility of biogas as a renewable energy source.
Moreover, the generator technology has evolved to become more efficient and user-friendly, making biogas a viable option even for smaller communities and individual households. The advancements in biogas technology are a testament to human ingenuity and our commitment to finding eco-friendly energy solutions.
In essence, biogas generators are not just about producing energy; they are about creating a sustainable future. They exemplify how we can harmoniously coexist with our environment, turning waste into wealth and challenges into opportunities. As we look forward to a greener future, the biogas generator stands out as a beacon of hope and innovation.
Reference List
(1) (2) 'Waste-to-Renewable Energy Transition: Biogas Generation for Sustainable Development' by Desire Wade Atchike, Muhammad Irfan, Munir Ahmad, and Mubeen Abdur Rehman is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
No changes were made to the material.
---------
(3) Paolini V, Petracchini F, Segreto M, Tomassetti L, Naja N, Cecinato A. Environmental impact of biogas: A short review of current knowledge. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2018 Aug 24;53(10):899-906. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2018.1459076. Epub 2018 Apr 13. PMID: 29652205.
