What are the pros and cons of Hydroelectric Power?
What Are The Pros and Cons of Hydroelectric Power?
What Are The Pros and Cons of Hydroelectric Power?
Where our energy future hinges on balancing sustainability with practicality, hydroelectric power emerges as a significant contender. This form of renewable energy, harnessed from the strong water currents and natural water flow behind massive structures like the Hoover Dam, taps into the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity.
While the establishment of hydroelectric power plants, symbolised by iconic dams, presents a myriad of advantages, it also brings with it certain drawbacks. From its role as a clean energy source that combats greenhouse gases and reduces reliance on fossil fuels, to the sometimes controversial environmental impacts associated with creating large reservoirs, hydroelectric power presents a nuanced landscape. It embodies a fusion of traditional ingenuity and contemporary environmental awareness, showcasing the diverse advantages and disadvantages inherent to hydropower.
In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of hydroelectric power in depth, aiming to provide a balanced perspective on its role in our quest for sustainable energy solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Renewable and Efficient Energy Source: Hydroelectric power is highlighted as a significant and reliable renewable energy source. It's emphasised by the comparison of the efficiency of hydroelectric power (up to 90% efficient) with other renewable sources like solar and wind. The content also points out how hydroelectric facilities, such as pumped storage plants, provide enhanced energy reliability and adaptability.
- Environmental and Social Considerations: While hydroelectric power offers substantial environmental benefits like low emissions and reduced fossil fuel reliance, it also poses notable environmental and social challenges. These include the potential disruption of local ecosystems, impacts on water flow and quality, and the displacement of communities. The necessity of conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) and considering the broader ecological and societal impacts is underscored.
- Economic and Land Use Impact: The content discusses the economic efficiency of hydroelectric power, noting its long-term cost benefits compared to other energy sources. However, it also acknowledges the high initial costs and the intensive resource and land requirements for establishing hydroelectric plants. The multifunctionality of hydroelectric facilities, serving purposes beyond energy generation like irrigation and flood control, is also highlighted.

What is Hydropower?
Hydropower, a remarkable form of renewable energy, has been harnessing the power of water to generate electricity for decades. At the heart of this process are hydroelectric plants, where dams play a crucial role. By controlling water flow, these dams enable the conversion of water's kinetic energy into electricity. It's not just about generating power; hydropower is intertwined with the water cycle, contributing to energy sources globally. However, it's not without its challenges. Issues like the environmental impact of reservoir creation, the reliance on consistent water flow (which can be affected by droughts), and the production of greenhouse gases like methane from reservoirs, pose significant concerns.
What Is Hydroelectricity And How Does It Work?
To truly grasp the essence and functionality of hydroelectric power, it's crucial to understand its foundational principles. Hydroelectricity is a form of clean energy generated by the movement of water through turbines, a process deeply rooted in both nature's cycle and human engineering. This renewable energy source stands as a testament to our ability to harness natural forces in a way that lights up our cities while maintaining a commitment to environmental stewardship. For a comprehensive exploration, What Is Hydroelectricity And How Does It Work? An Overview, delves into the specifics of how dams orchestrate the flow of water to power turbines, the evolution of this technology, and its role in a sustainable energy future.
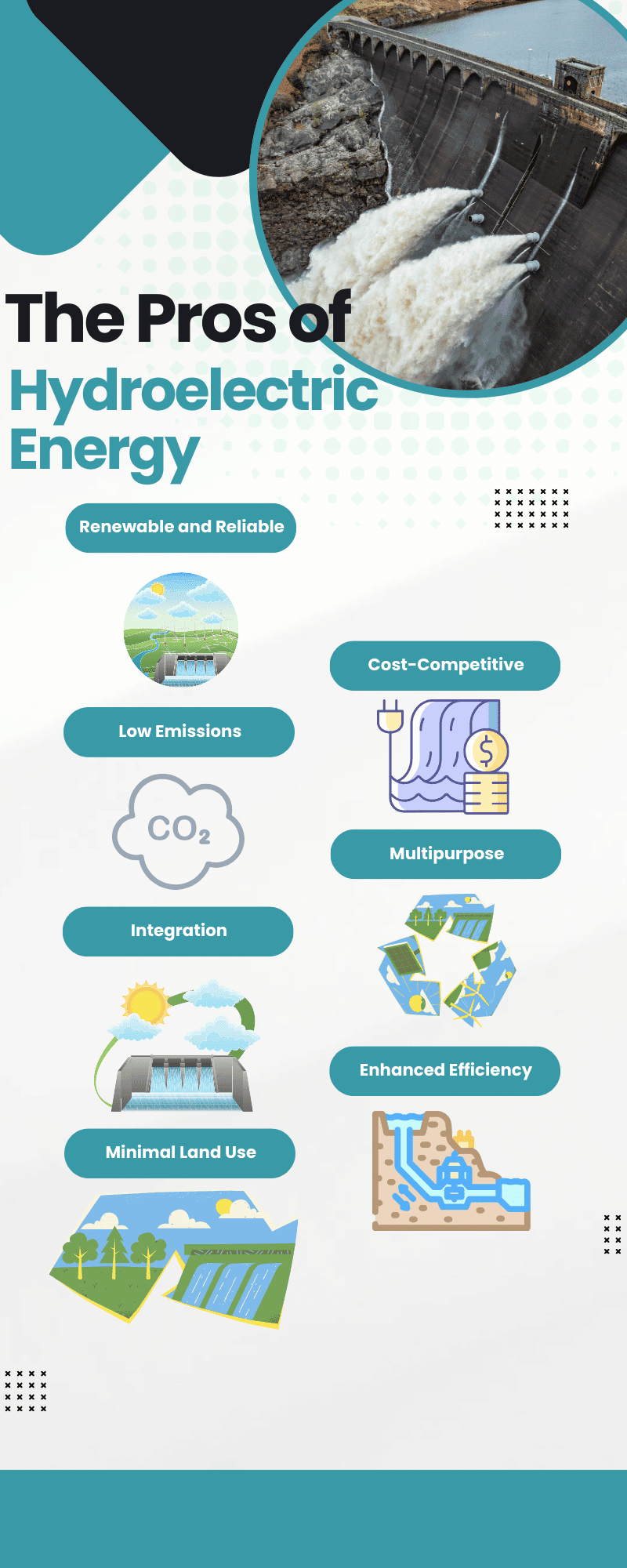
What are the Pros of Hydroelectric Energy?
Hydroelectric energy provides many advantages. Let's look at how this age-old technology is still relevant and advantageous today.
- Renewable and Reliable
Classified as a renewable energy source, hydroelectric power is generated by the endless cycle of water, making it a reliable and constant source of energy. China's Three Gorges Dam is a prime example of hydroelectric power's reliability and renewability. Utilising the Yangtze River, this massive structure generates about 22,500 MW, showcasing the immense potential of renewable hydroelectric energy.
- Cost-Competitive Energy Source
Compared to other energy sources, hydroelectric power has been historically cost-effective, offering a sustainable solution to energy demands without breaking the bank.
- Low Emissions
Hydroelectric plants produce significantly less carbon dioxide and methane than fossil fuels, making them a greener alternative for electricity generation. Brazil, harnessing its extensive river systems for hydroelectric power to produce around 70% of its electrical energy, significantly reduces its greenhouse gas emissions, exemplifying the environmental benefits of this energy source.
- Multipurpose Facilities
Beyond energy generation, many hydroelectric facilities are used for recreational purposes and can also serve as water reservoirs. Egypt's Aswan High Dam not only generates power but also supports irrigation and provides flood control, illustrating the multifaceted benefits of hydroelectric facilities.
- Integration with Other Renewable Sources
Hydroelectric power can be combined with other renewable sources like solar power, enhancing the overall efficiency of energy generation. Portugal successfully integrates hydroelectric with wind and solar energy, achieving impressive renewable energy milestones and setting an example for global energy strategies.
- Pumped Storage for Enhanced Efficiency
Pumped storage hydropower plants improve energy storage capabilities, making hydroelectric energy more reliable and adaptable to varying demands. The UK's Dinorwig Power Station uses pumped storage to regulate energy supply, highlighting how hydroelectricity can adapt to fluctuating energy needs.
- Minimal Land Use Once Established
Once established, hydroelectric plants require relatively little land compared to other power plants, reducing their environmental footprint. India's push for small-scale hydroelectric projects demonstrates how this energy source can be harnessed with minimal land use, even in densely populated regions.
Beyond its general advantages, hydroelectric energy offers specific environmental and economic benefits worth highlighting as we strive for a sustainable future.
What are the Environmental and Economic Benefits of Hydroelectric Energy?
Hydroelectric energy offers a plethora of environmental and economic benefits. Let's dive into the many pros of this remarkable energy source.
- Renewable and Reliable: Hydropower is like the sun - always there, always reliable. It's a renewable source that doesn't deplete our planet's resources, ensuring a sustainable future.
- Economic Efficiency: Building hydroelectric facilities is a long-term investment with low operational costs. It's like planting a seed and reaping the benefits for years to come. The case study, titled "Energy Efficiency Technologies for Hydroelectric Power Plants: A Case Study in Brazil," explores the optimisation of energy use in a Brazilian hydroelectric plant. The study aims to enhance energy efficiency and propose improvements for the rationalisation of energy application. By evaluating the systems associated with energy generation, the study identifies potential advantages, estimating savings of 2910 MWh/year in electricity consumption for the plant itself. This is achieved through better equipment utilisation and the possibility of increasing the power generated. The case study underscores the significance of hydroelectric power in Brazil's energy matrix and highlights the economic and environmental benefits of optimising energy use in hydroelectric facilities (1).
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Producing energy without burning fossil fuels, hydropower is a champion in the fight against climate change.
- Generation Stability: With hydroelectric power, energy generation is as steady as a ticking clock, providing a stable source of power for communities and industries alike.
- Minimising Reliance on Fossil Fuels: By tapping into hydropower, we reduce our dependency on non-renewable energy sources, paving the way for a greener tomorrow.
- Adaptability to Demand: Hydroelectric facilities can adjust to fluctuating energy demands, making them as flexible as they are powerful.
While the benefits of hydroelectric energy are significant, it's important to also consider the challenges and drawbacks that accompany its use.
What are the Cons of Hydroelectric Power?
Hydroelectric power, often lauded for its benefits, has its share of drawbacks. Let's explore these disadvantages to get the full picture.
- Environmental Disruption: Building dams can significantly alter natural waterways, affecting local ecosystems and wildlife. The case study titled "Environmental Impact of Small Hydro Power Plant—A Case Study" focused on evaluating the environmental impacts of constructing a small hydroelectric power plant in Spišské Bystré, Slovakia. It assessed how the plant's construction and operation would influence the surrounding ecosystem. The findings underscore the critical role of conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) before initiating such projects. This preemptive evaluation is vital for identifying and mitigating potential environmental damages, ensuring sustainable project development. The conclusion drawn from the study advocates for the necessity of EIAs in the planning stages to minimise adverse environmental effects and avoid escalated costs associated with unforeseen environmental issues (2).
- Reliance on Climatic Conditions: Since hydropower depends on water flow, it can be less reliable in areas prone to droughts. It's not a one-size-fits-all solution.
- Social Impact: Large projects can displace communities, often without adequate resettlement plans. It's a human cost that sometimes goes unnoticed.
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for hydroelectric infrastructure is substantial. It's a financial mountain to climb.
- Methane Emissions: Stagnant water in reservoirs can lead to the decomposition of organic material, releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Not so clean after all.
- Maintenance and Operational Risks: Dams require constant maintenance, and failures can have catastrophic consequences. It's a responsibility that weighs heavy.
- Long-term Ecological Changes: Altering water flow can lead to long-term changes in sedimentation patterns and water quality, affecting downstream ecosystems.
The drawbacks of hydroelectric power segue into broader issues of global water concerns, underscoring the complex relationship between hydropower development and water resource management.
Hydropower and Global Water Concerns
Hydropower is a key player in our quest for renewable energy, but it's deeply connected to important water issues worldwide. This section explores how hydropower interacts with major water concerns, including scarcity, rights, and international disagreements.
Water Scarcity and Hydropower
Around the world, water scarcity affects billions, worsened by changes in climate, growing populations, and increased demand for water. Hydropower projects, while providing clean energy, can impact water availability, changing how much water is available underground and the natural flow of rivers. It's crucial to find a balance between using water for energy and keeping enough water for people and nature, ensuring hydropower is sustainable and doesn't harm water supplies.
Water Rights and Hydropower
Water rights, which are the rules about who can use water, are essential when building and running hydropower plants. When water is shared for different uses—like farming, factories, and homes—using it for hydropower can cause conflicts. It's important to create rules that allow hydropower to work without removing water from others, respecting everyone's needs and the environment.
International Disputes and Hydropower
Hydropower can cause arguments between countries, especially when they share rivers. If one country builds a hydropower plant upstream, it can affect water availability downstream in another country. The debate over the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) among Egypt, Ethiopia, and Sudan is a clear example of how these issues can arise. Countries need to work together to manage shared water resources fairly and sustainably when planning hydropower projects.
Towards Sustainable Hydropower
To tackle these water issues, the hydropower industry must adopt sustainable practices, including:
- Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): This approach helps ensure hydropower development considers all different water needs, aiming for efficient and fair use.
- Environmental Flow Requirements: Maintaining enough water flow downstream of dams is crucial to protect ecosystems and the services they provide to humans.
- International Cooperation: Countries sharing rivers need to collaborate to develop hydropower in a way that benefits everyone and reduces the chances of conflict.
- Innovative Technologies: Using new technologies can help reduce water use and environmental impact, making hydropower more sustainable.
As we grapple with these water-related challenges, it's crucial to look ahead and contemplate the evolving landscape of hydroelectric power and its role in our energy future.
The Future of Hydroelectric Power
Hydropower is not just a renewable energy source; it's a beacon of innovation in the sustainable energy landscape. Its prowess in generating electricity from the flow of water places it in the league of traditional sources like coal, yet it stands out for its renewable nature and ability to produce clean, cost-competitive energy.
Recent advancements in hydropower technology are propelling it to new heights. For instance, the development of small-scale, low-impact hydroelectric projects offers a more environmentally sensitive approach, minimising ecosystem disruption. Innovations like fish-friendly turbines are addressing ecological concerns by allowing safe fish passage. Furthermore, modern hydroelectric plants are exploring the integration of pumped-storage systems, which act like giant batteries, storing excess energy and releasing it when demand peaks.
The challenges, primarily the environmental impacts of large-scale dams and the need for substantial water volumes are being met with evolving solutions and careful management. These advancements make hydroelectric power not just a legacy of the past, but a dynamic, evolving source of clean energy for the future.
FAQ on Hydroelectric Energy
Hydroelectric energy is primarily used for generating electricity. It powers homes, businesses, and industries. Additionally, hydroelectric facilities can provide water for irrigation and drinking, and offer recreational opportunities like fishing and boating.
Hydroelectric power is highly reliable. It provides a consistent energy supply, as water flow can be controlled through dams. Unlike solar or wind energy, it's not as dependent on weather conditions, making it a stable power source.
No, hydroelectric power is considered a renewable energy source because it uses the Earth's water cycle. As long as the water cycle continues, hydroelectric power can be generated.
The main advantages include its renewable nature, low operational costs, and minimal greenhouse gas emissions. It also has the ability to quickly adjust power output to meet electricity demand.
Yes, while hydroelectric power is environmentally friendly, it can have impacts such as altering river ecosystems, affecting fish migration, and displacing local communities due to dam construction.
Evaluating Hydropower: The Intersection of Advantages, Disadvantages, and Energy Potential
We've navigated through the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric energy. This energy source, celebrated for its sustainability and efficiency, also faces scrutiny over environmental and social impacts. Hydroelectric power, with its renewable essence and potential for low operational costs, stands as a testament to human ingenuity in harnessing nature's forces. Yet, the environmental disruptions and social displacements it can cause remind us of the need for balance and careful planning. As we look to the future, the evolution of hydroelectric technology—towards minimising ecological harm and maximising efficiency—promises a brighter, cleaner energy landscape.
Reference List
(1) Bimestre, T.A., Mantovani Júnior, J.A., Canettieri, E.V., Tuna, C.E. and Sobrinho, P.M. (2022) Energy Efficiency Technologies for Hydroelectric Power Plants: A Case Study in Brazil. Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 10, 90-115. doi: 10.4236/jpee.2022.105007.
No changes were made to the material.
---------
(2) Zeleňáková, M.; Fijko, R.; Diaconu, D.C.; Remeňáková, I. Environmental Impact of Small Hydro Power Plant—A Case Study. Environments 2018, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5010012
Research licensed under CC BY 4.0 DEED.
No changes were made to the material.
